Meet Regulatory Requirements to Ensure Patient Safety
Developing and validating a robust freeze/thaw process while meeting regulatory guidelines is a multifaceted challenge. The demand for cold chain processes and operations for biopharma products is increasing due to scaling of complex therapeutics, a challenging global supply chain, and growing shipping complexities. Ensuring compliance throughout the product journey is integral to mitigating risk for product loss and contamination.
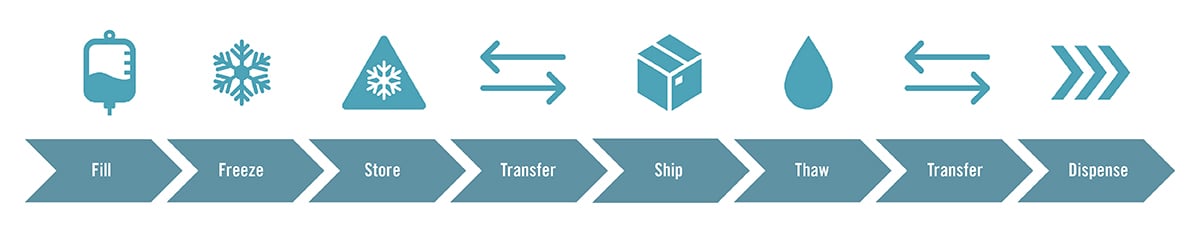 The cold chain process can be explained in terms of:
The cold chain process can be explained in terms of:
- Fill: Automating or manually delivering your solution
- Freeze: Cooling down your solution by blast or plate freezer, this is also critical for thawing since biologics are temperature sensitive.
- Store: Both bags and bottles are typical solutions for storing high-value products.
- Transfer and Ship: Product withstanding temperature, vibration, and movement during travel is critical in terms of preserving product aseptic boundaries and eliminating the possibility of product loss.
- Thaw: In many cases, the same freezers that are used to freeze are also used to thaw. The biggest change during this step is proving drug reliability since biologics are temperature sensitive.
- Transfer: Manual movement of product is a potential point of failure. Using a facility trolly is a next logical step but it is important to understand how this fits within your process regarding safety, staffing, and stability.
- Dispense: Contamination is the major concern, but with the right connectors and single-use solutions, contamination can be prevented. In addition, Aramus™ single-use solutions have the maximum extraction rate of any single-use system (SUS) at 99%.
Safety, purity, and efficacy are critical product quality attributes that are protected with a validated freeze/thaw workflow. Customers need controlled, consistent, and scalable solutions to sustain those critical attributes. The greatest risks during sensitive freeze/thaw process are:
- Protein degradation
- Protein aggregation
- Cryoconcentration
- Ice nucleation
- Container integrity
- Product contamination
From bottles to stainless steel containers to bags, there are many single-use assemblies that can help protect your product during a freeze/thaw process. Considerations when determining what containment to use in your process:
- Robustness
- Multi-use
- Weight and bulk for shipping
- Cleaning and validation requirements
- Low freezer utilization/optimization
- Leaky seams and tubing
- Gamma sterilizable
We understand the complexities of single-use solutions for bulk freeze/thaw and transport, and partner with our customers to understand their unique needs. In delivering customized solutions backed by a global infrastructure, customers obtain valuable outcomes. Our world-class Life Sciences Technology Center is dedicated to offering customers access to experts who, with their deep knowledge of testing, equipment, and containment, will guide you through freeze/thaw process optimization strategies.
Learn more about how we can help.




